Synchronisation Channel
A sync channel is a set of instructions to synchronise some files between a hub and one of its connected storage, in one direction, using rsync. It is made of:
- a filter, to make a selection of the folders and the files concerned,
- options, to analyse the files and to control the transfers when some differences are found between the source and the destination.
Multiple channels can be defined per storage. They are processed sequentially (not at the same time) one after the other by a sync agent. A sync agent is an independent process, dedicated to a storage, ran in parallel, one for each storage. This way, we achieve a multi-directional, asynchronous synchronisation experience, hot-plugging storages, and fault-tolerant (a storage becoming offline don't interfere with the others storages).
Note
The hub, storages and channels can be represented as a tree:
hub/
├── storage1/
│ ├── chan
│ ├── chan
│ └── chan
├── storage2/
│ ├── chan
│ ├── chan
│ └── chan
└── storage3/
├── chan
├── chan
└── chan
The navigation bar lets you navigate between the elements using a clickable hierarchy-like path:

The navigation bar is composed of these elements:
- The hierarchy-like path:
hubstoragechannel - Contextual help (clickable) containing the short explaination about channels, and a link to this documentation.
- The activity and the direction of the channel. A up arrow means that the storage is sending to the hub (upload), a down arrow means the storage is receiving (download). A blinking arrow means that the channel synchronisation is in progress.
- A toggle button to toggle the channel on and off. When toggled on (), the channel will be read by the synchronisation when it comes to its turn in the process loop. When toggled off (), the channel will not be read and will be skipped when the processing agent will reach its turn in the sequence. Toggling off a in-progress channel don't kill the ongoing synchronisation process, it waits until the rsync process finishes, then won´t start it until it is switched on again.
Channel Main Panel
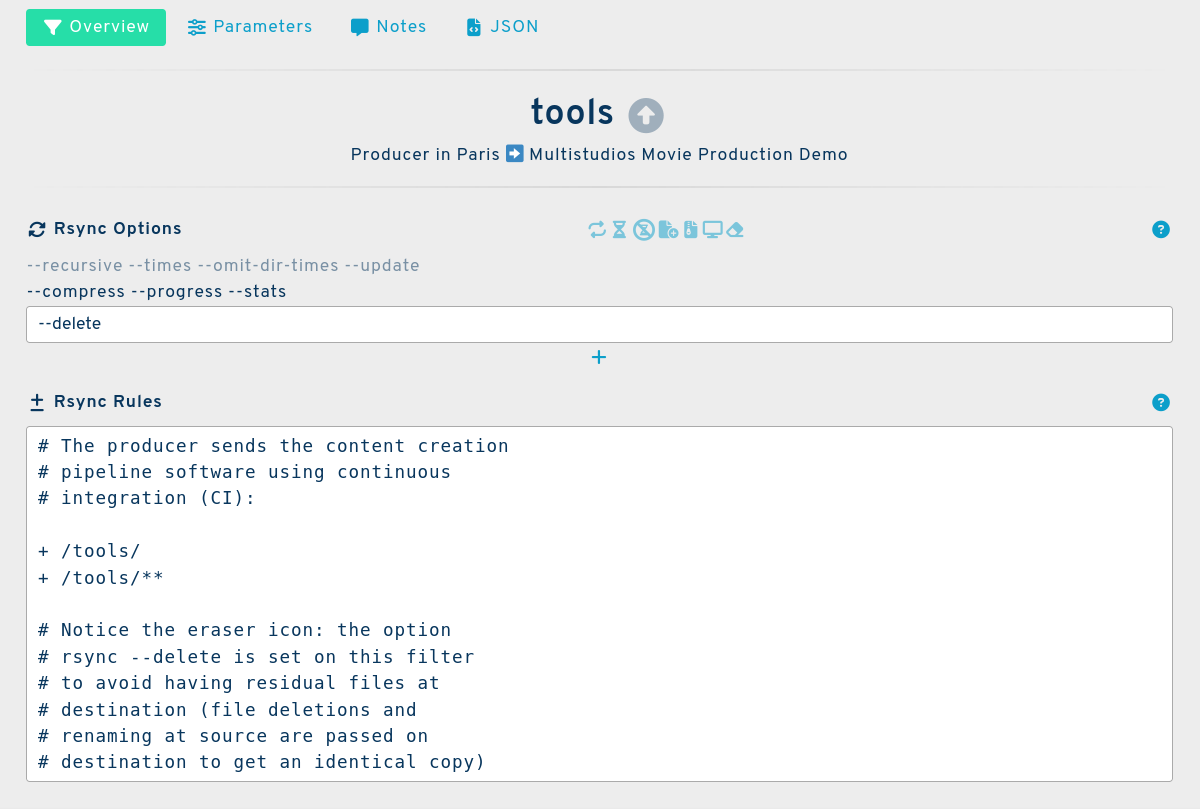
You can control many aspects of the file transfer using rsync options and filter rules.
Options
The options specified on a channel affect only this channel. In this example the --delete option is defined to clean the destination from unwanted files.
# The option: rsync --delete is set (see the
# eraser icon) to have an identical copy at
# destination (local file deletion and
# renaming at source are passed on
# destination)
Read the rsync options section for more details about the available options.
Rules
The rules are written using the rsync syntax to include or skip files and folders:
# The producer sends the software for the
# pipeline in continuous integration (CI):
+ /tools/
+ /tools/**
Read the dedicated rsync filters section for details about the syntax and how they work in SyncPlanet.
Channel Parameters
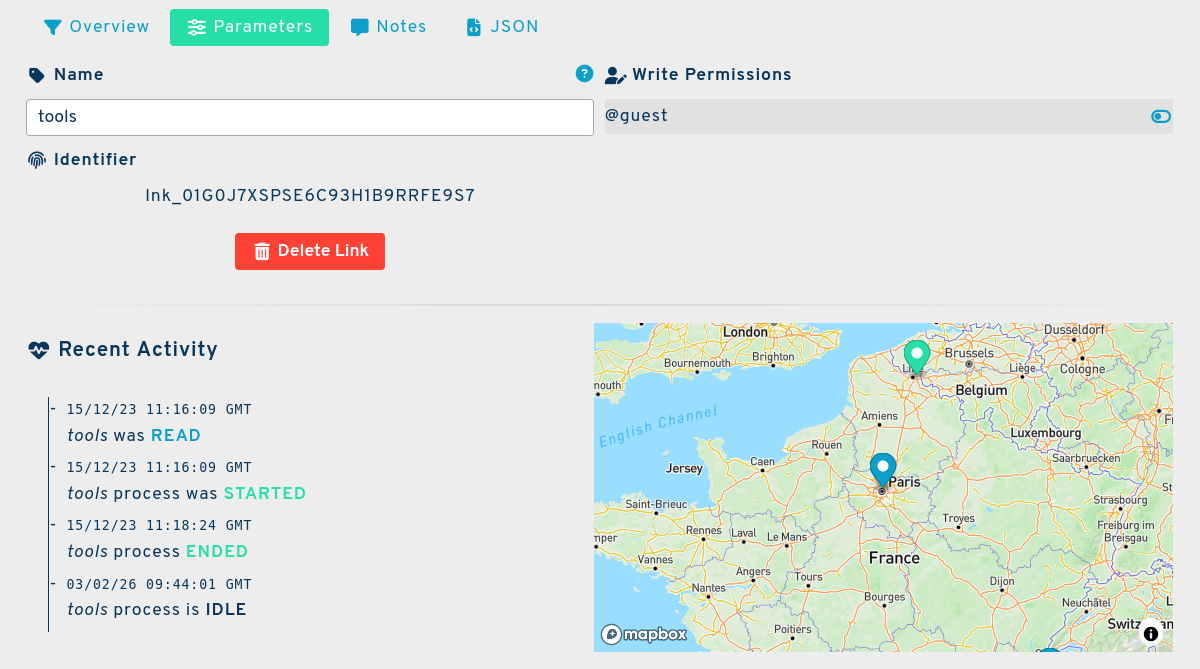
Name
Note
A name, at your convenience, without character restriction, to name the element in the interface instead of naming it with its _id
Tip
Example:
tools
Identifier
Note
An automatically generated string to identify the link of the form: lnk_# where # is a Universally Unique Lexicographically Sortable Identifier .
Tip
Example
lnk_01G0J7XSPSE6C93H1B9RRFE9S7
Write Permissions Table
SyncPlanet is multi-user: only the users specified as authors can write and update an object.
Note
If a user is not proposed in the table, it means that you first have to connect him/her to the project
Note
Developers can access the permissions table under the author key which can have a single user string value or have multiple user names in an array of username strings.
Status
The status is a bunch of information on links, to know when was the last run, the duration, and showing the possible errors encountered in the process.
Channel Programming Interface
A channel and its properties can be accessed as a JSON object:
{
"_id": "lnk_01G0J7XSPSE6C93H1B9RRFE9S7",
"author": "support",
"enable": true,
"include": "# The producer sends the software for the\n# pipeline in continuous integration (CI):\n\n+ /tools/\n+ /tools/**\n\n# The option: rsync --delete is set (see the\n# eraser icon) to have an identical copy at\n# destination (local file deletion and\n# renaming at source are passed on\n# destination)",
"name": "tools",
"rsync_args": "--delete",
"src_id": "vol_01FWEWD03P3J2H98TQ0Y4AXF3H",
"tgt_id": "hub_01FX33ZYB78E9F5FTZMKC96A4P",
"time": 1649879738073,
"timeBegin": "2023-12-15 11:16:09+00:00",
"timeEnd": "2023-12-15 11:18:24+00:00",
"timeRead": "2023-12-15 11:16:09+00:00"
}
Please read Environment-Setup and API for details about how to setup a client programming environment.
Next
You might continue reading:
- Try the demo channel,
- Continue reading the documentation about the storages,
- Continue reading about the hubs.